Advanced SMT PCBA Manufacturing and Assembly Solutions
SMT PCBA manufacturing is the backbone of modern electronic product production, enabling compact designs, high component density, and reliable performance in electronic products across various industries, including automotive, industrial control, medical equipment, and consumer electronics.

What is a PCBA in manufacturing?
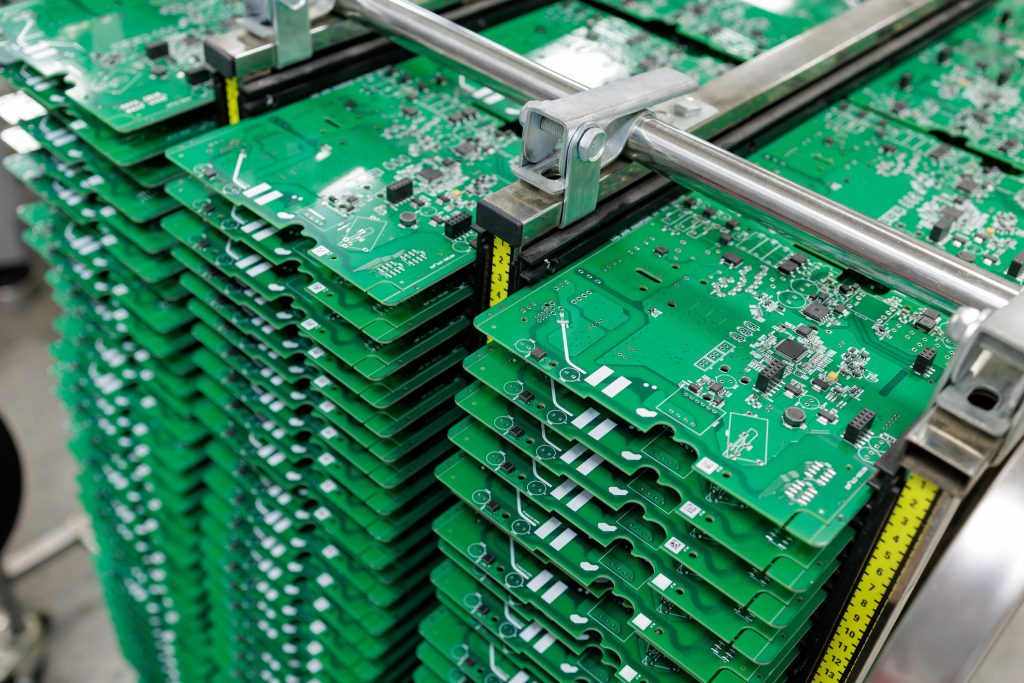
PCBA stands for Printed Circuit Board Assembly. In manufacturing, it refers to a bare PCB after electronic components are mounted and soldered onto it. The board is no longer just a mechanical platform. It becomes a working electronic unit that can be tested, programmed, and integrated into a final product.
A PCB on its own contains copper traces, pads, and vias. It cannot perform any function. PCBA manufacturing adds value by placing resistors, capacitors, ICs, connectors, and other parts onto the board in precise locations. Once soldered, these components form complete electrical circuits.
In modern factories, PCBA manufacturing is treated as a system rather than a single step. It includes material control, assembly execution, inspection, and functional validation. Each activity affects yield and long-term reliability. That is why advanced SMT PCBA manufacturing focuses on repeatable outcomes, not just assembly speed.
What is the SMT process in PCBA?
The SMT process in PCBA describes how surface mount components are placed and soldered onto a PCB. Unlike older through-hole methods, SMT places components directly onto surface pads. This allows smaller parts, higher density, and faster automated assembly.
An SMT PCBA process usually begins with solder paste printing. A stencil applies solder paste onto each pad with controlled volume. Accuracy here is critical. Too much paste can cause shorts. Too little can weaken joints.
After printing, pick-and-place machines position components onto the pasted pads. These machines work at high speed while maintaining tight placement tolerance. Advanced SMT machines can handle tiny passive parts, fine-pitch ICs, and complex packages in the same run.
The populated board then enters a reflow oven. Controlled heat melts the solder paste and forms permanent joints. Temperature profiles are carefully tuned to suit component limits and solder chemistry. Once cooled, the board exits the oven as a completed SMT assembly.
Post-reflow inspection verifies solder quality and placement accuracy. Automated optical inspection is common, while X-ray inspection is used for hidden joints like BGAs.
How many types of PCBA are there?
PCBA types are often classified by assembly method and application needs. Common PCBA types include:
- SMT PCBA: Uses surface mount components on one or both sides of the PCB. This is the most widely used approach today due to its efficiency and compact layout support.
- Through-hole PCBA: Components with leads pass through drilled holes and are soldered on the opposite side. This method is still used for connectors and parts that need strong mechanical anchoring.
- Mixed-technology PCBA: Combines SMT and through-hole components on the same board. Many industrial and power designs rely on this hybrid approach.
- Single-sided PCBA: Components are mounted on one side of the board only. This is common for simple control boards or cost-sensitive designs.
- Double-sided PCBA: Components are mounted on both sides. This approach increases functional density without increasing board size.
Each type places different demands on equipment, process control, and inspection. Advanced SMT PCBA manufacturing solutions are designed to support all of these configurations with stable quality.
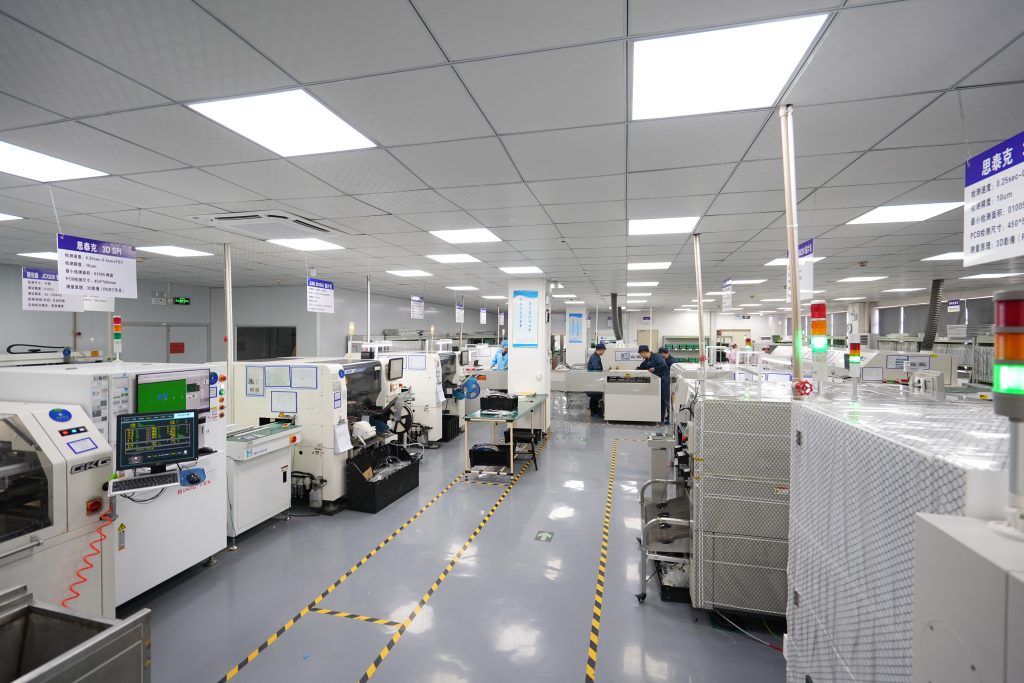
What is an SMT line in manufacturing?
An SMT line is the physical production line where surface mount assembly takes place. It is not a single machine, but a coordinated sequence of equipment working together.
A typical SMT line includes a solder paste printer, pick-and-place machines, a reflow oven, and inspection systems. Boards move through this line in a controlled flow.
Modern SMT lines are highly automated. They rely on feeders, vision systems, and software integration to maintain accuracy. Data from each machine can be collected to track yields and detect trends early.
An advanced SMT line is also flexible. It can switch between products quickly with minimal downtime. This flexibility supports prototypes, low-volume builds, and mass production on the same infrastructure.

What are the phases of SMT?
The SMT process can be divided into clear phases. Each phase has a specific purpose and quality focus.
The main phases include:
- Material preparation: Components are checked, baked if needed, and loaded into feeders. PCBs are verified for cleanliness and flatness.
- Solder paste printing: Paste is applied through a stencil onto PCB pads. Printing accuracy sets the foundation for solder joint quality.
- Component placement: Pick-and-place machines position components onto the pasted pads. Vision systems verify alignment during placement.
- Reflow soldering: Boards pass through a controlled heating profile. Solder melts, wets the pads, and forms joints.
- Inspection and verification: AOI and X-ray systems inspect solder joints and component placement. Defects are flagged for correction.
Each phase contributes to final yield. Advanced SMT PCBA manufacturing focuses on balancing these phases to avoid hidden weaknesses that only appear during field use.
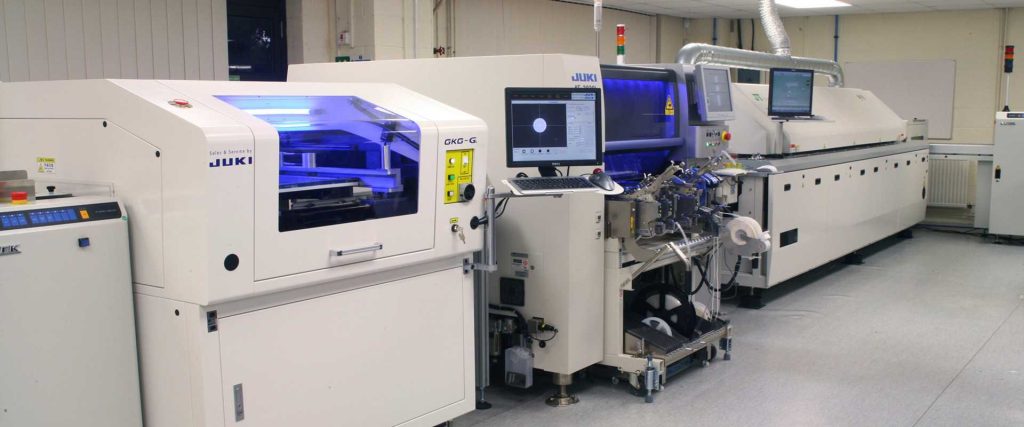
What equipment is used in SMT assembly?
SMT assembly relies on a set of specialized machines, each performing a defined task.
Key SMT equipment includes:
- Solder paste printers: These machines apply paste with precise thickness and alignment.
- Pick-and-place machines: They place components at high speed and high accuracy.
- Reflow ovens: Multi-zone ovens control heating and cooling rates. Nitrogen reflow is often used to improve solder joint quality.
- Automated optical inspection systems: AOI checks for missing parts, polarity errors, and solder defects after reflow.
- X-ray inspection machines: Used for hidden joints such as BGAs and QFNs. They reveal voids and bridges not visible optically.
Supporting equipment such as loaders, unloaders, and conveyors ensures smooth board flow. In advanced SMT PCBA manufacturing, equipment selection is driven by product requirements.

What is the difference between PCB and SMT?
PCB and SMT are closely related but serve different roles in electronics manufacturing. A PCB is the physical board. SMT is a method used to assemble components onto that board.
The PCB defines layer count, material, thickness, and copper layout. It is fabricated before any components are added. SMT comes later and focuses on how parts are mounted and soldered.
Another difference lies in responsibility. PCB fabrication is about structural accuracy and electrical integrity. SMT assembly is about placement precision and solder joint reliability.
What industries use SMT?
SMT is used across nearly every electronics-driven industry. Its flexibility and efficiency make it suitable for both high-volume and specialized products.
Industries that rely heavily on SMT include:
- Consumer electronics: Smartphones, wearables, and home devices depend on compact SMT assemblies.
- Industrial control: Automation systems and controllers require stable SMT PCBA manufacturing with long product lifecycles.
- Automotive electronics: Control units, sensors, and infotainment systems use SMT for density and reliability.
- Medical devices: Diagnostic and monitoring equipment demand clean processes and traceable SMT assembly.
- Telecommunications: Networking hardware and base stations rely on high-speed SMT PCBA designs.
- Aerospace and defense: Ruggedized SMT assemblies support mission-critical systems.
Across these sectors, efficient SMT PCBA manufacturing solutions enable faster innovation and dependable supply.

Conclusion:
SMT PCBA manufacturing is the backbone of modern electronics production. It transforms bare PCBs into functional assemblies through precise placement, controlled soldering, and thorough inspection.
If you are planning a new project or reviewing your current SMT PCBA manufacturing strategy, professional guidance makes a difference. For technical consultation or project inquiries, contact sales@bestpcb.vn
 language
language

