PCBA Traceability for Reliable Manufacturing and Quality Control
PCBA traceability is the systematic recording and tracking of every component, material, and process step involved in the assembly of a Printed Circuit Board Assembly (PCBA). This article explores how robust traceability ensures manufacturing reliability, stringent quality control, and compliance across critical industries.
What Are The Most Pressing Challenges OEMs Face When Bringing A PCBA To Market?
- Black Box Production: No visibility into process history
- Counterfeit Components: Unverified parts in the supply chain
- Broad Recall Exposure: Inability to isolate affected batches
- Compliance Friction: Manual, error-prone audit preparation
- Inefficient RMA Handling: Slow diagnosis without build history
End-to-end digital traceability converts these risks into controlled, data-driven manufacturing execution.
- Full Process Transparency: Unit-level production records
- Verified Component Genealogy: Authentic parts from source to board
- Targeted Recall Control: Machine-, shift-, or reel-level isolation
- Automated Compliance Records: Audit-ready reports on demand
- Faster RMA Resolution: Instant access to complete build data
At EBest Circuit (Best Technology), we integrate advanced traceability not as an afterthought but as the core of our manufacturing execution system (MES). As a professional PCBA manufacturer specializing in complex and high-reliability projects, we build transparency and accountability into every board we produce, ensuring our clients receive products they can trust. For inquiries, pls feel free to contact us at sales@bestpcb.vn.

What Is PCBA Traceability And Why Does It Matter In Manufacturing?
PCBA traceability refers to the ability to document and follow the history, application, and location of a product and its components through all stages of manufacturing, from raw material to finished good. It matters because it transforms manufacturing from a “black box” into a transparent, data-rich process.
- Risk Mitigation: It enables rapid containment of non-conforming materials, preventing defective units from reaching the market.
- Process Optimization: By analyzing traceability data, manufacturers can identify bottlenecks, solder defects, or machine inefficiencies.
- Regulatory Mandate: Industries like automotive (IATF 16949) and medical (ISO 13485) have strict traceability requirements.
- Brand Protection: It safeguards brand reputation by providing proof of diligence and control over the supply chain.
- Lifecycle Management: Supports activities like warranty validation, field updates, and end-of-life component management.
In essence, PCBA traceability is the foundational capability for modern, responsible, and efficient electronics manufacturing, directly enabling reliable quality control.
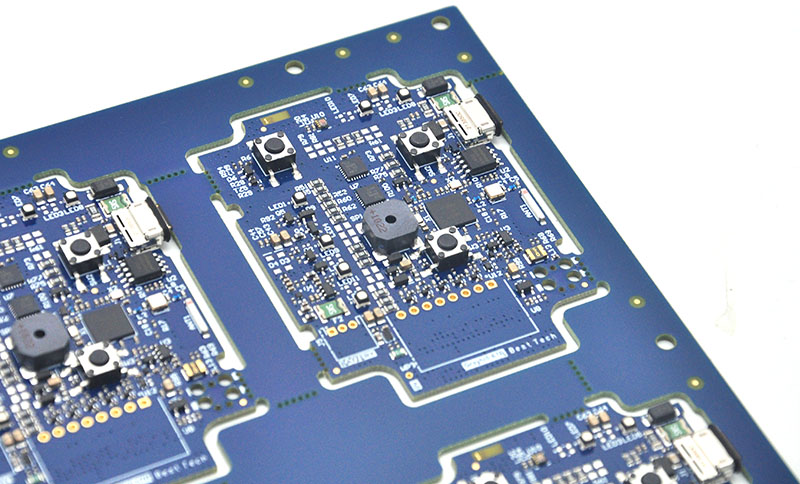
How Does PCB Traceability Ensure Material Compliance And Incoming Quality?
PCB traceability begins at the earliest stage of the supply chain, long before assembly starts.
It ensures that every laminate, prepreg, and copper foil entering production meets defined specifications and compliance requirements, forming the foundation for stable PCBA manufacturing.
A traceability-driven incoming quality control (IQC) process focuses on linking materials, data, and decisions, rather than relying on isolated inspections.
Key PCB Traceability Actions In Incoming Quality Control
| Traceability Action | Quality Focus |
|---|---|
| CoC Batch Linking | Regulatory compliance |
| First-Article Data Logging | Dimensional accuracy |
| Supplier History Tracking | Source consistency |
| Material Storage Tracking | Shelf-life control |
| Lot-Based Process Control | Process stability |
These actions allow manufacturers to associate each PCB material batch with its compliance status and performance history, rather than treating materials as interchangeable inputs.
For example, linking supplier batch numbers to Certificates of Conformance (CoCs) enables rapid verification against RoHS, REACH, or UL requirements.
First-article inspections capture critical parameters such as trace width and dielectric thickness, ensuring materials meet design intent before full production begins.
Supplier performance data accumulated through traceability records supports objective sourcing decisions and early risk identification.
Tracking storage conditions and shelf life prevents expired or degraded materials from entering production, while lot-specific process adjustments help maintain consistency when material characteristics vary.
This level of PCB traceability ensures that non-compliant or substandard materials are identified and isolated at the incoming stage, protecting downstream PCBA yield, reliability, and customer requirements.
How Do BRC Traceability Requirements Apply To PCB And PCBA Production?
The British Retail Consortium (BRC) Global Standard for Consumer Products emphasizes rigorous traceability requirements to ensure product safety and integrity. While often associated with food, its principles are directly applicable to consumer electronics like PCBAs, where safety is paramount (e.g., chargers, appliances).
For PCB and PCBA production, BRC-like requirements translate to:
- Unique Identification: Every batch of raw material (copper clad laminate, components) and every production lot must have a unique identifier.
- Chain of Custody: The system must record every transfer and transformation—from which reel of components was used on which machine at what time, to which finished goods lot the board was packed into.
- Forward & Backward Trace: Ability to trace any finished product back to all its constituent materials (backward) and any material batch forward to all products that contain it.
- Time-Bound Response: The traceability system must allow for the simulated or actual execution of a product recall within a defined, short timeframe (e.g., 4 hours).
- Audit-Verifiable Records: All traceability data must be maintained in clear, accessible records for external audit purposes.
Adhering to such stringent standards forces a discipline that elevates overall manufacturing quality and preparedness.
How Does PCBA Traceability Improve Quality Control And Risk Management?
PCBA traceability is the engine of a proactive quality control and risk management strategy. It moves quality from a final inspection checkpoint to a continuous, integrated process.
- Real-Time SPC (Statistical Process Control): Traceability links process data (e.g., reflow oven profile, solder paste inspection results) to each board. Deviations trigger immediate alerts, preventing mass defects.
- Closed-Loop Corrective Action (CLCA): When a test failure occurs, the system instantly retrieves the complete build record for that unit, accelerating root cause identification and corrective action implementation.
- Predictive Analytics: Historical traceability data can be analyzed to predict machine maintenance needs or identify components with higher early failure rates.
- Reduced Escapes: By enforcing checks at each stage (e.g., a component cannot be scanned unless the previous station passed), defective units cannot proceed unnoticed.
- Quantified Risk Scoring: Different product batches can be assigned risk scores based on factors like new component introductions, machine used, or operator, directing targeted inspection resources.
This data-centric approach systematically reduces variability and manufacturing risk.
What Data Should Be Included In A PCBA Traceability System?
An effective PCBA traceability system must capture a comprehensive digital thread. Essential data points include:
- Bill of Materials (BOM) Data: Component manufacturer, part number, lot/date code, and supplier source for every item.
- Process Data: Machine IDs (pick-and-place, reflow oven), operator IDs, timestamps, and critical process parameters (temperatures, speeds) for each operation.
- Inspection & Test Data: Results from Automated Optical Inspection (AOI), X-ray inspection, In-Circuit Test (ICT), and functional test, linked to the specific unit.
- Serialization Data: Unique identifiers at multiple levels—component reel, PCB panel, individual PCBA, and final product serial number.
- Non-Conformance Records: Details of any defects found, containment actions taken, and rework performed.
- Calibration & Maintenance Logs: Status of all manufacturing and test equipment to ensure results are valid.
- Packaging & Shipping Data: Linking final product serial numbers to shipping batches and customer destinations.
This holistic data set forms the complete “product genealogy.”
How Does MES-Based Traceability Improve PCBA Manufacturing Transparency?
A Manufacturing Execution System (MES) is the ideal platform for PCBA traceability, providing real-time, bidirectional communication between the shop floor and business systems.
- Single Source of Truth: The MES centralizes all traceability data, eliminating siloed spreadsheets or paper travelers prone to loss and error.
- Real-Time Visibility: Production supervisors can see the real-time status, yield, and location of every order and batch on dashboards.
- Automated Data Capture: Barcodes, QR codes, or RFID scanners automatically capture data at each station, ensuring accuracy and eliminating manual entry.
- Enforced Workflow: The system guides operators through the correct steps, preventing missed operations and ensuring process adherence.
- Integration with ERP & PLM: Seamlessly connects traceability data with order management (ERP) and design specs (PLM), providing full business context.
MES-based traceability creates unparalleled transparency, allowing for agile decision-making and continuous improvement.
Why Is PCBA Traceability Critical For Medical Projects?
In medical device manufacturing, traceability is not just a best practice—it is a legal and ethical imperative governed by standards like ISO 13485 and FDA 21 CFR Part 820.
- Patient Safety: Enables rapid, precise recalls of potentially faulty devices to prevent patient harm.
- Regulatory Compliance: Provides the documented evidence required for FDA audits and regulatory submissions.
- Unique Device Identification (UDI): Supports compliance with global UDI regulations, which mandate tracking devices throughout their distribution and use.
- Liability Protection: Creates an irrefutable record of due diligence in manufacturing, which is crucial in the event of an adverse incident.
- Post-Market Surveillance: Facilitates the investigation of field failures and the implementation of necessary field corrections.
For medical PCBA projects, traceability is the non-negotiable backbone of a quality management system.
How Does PCBA Traceability Support After-Sales And RMA Handling?
When a product fails in the field, efficient and accurate Return Material Authorization (RMA) handling is vital. PCBA traceability transforms this often-chaotic process.
- Instant History Retrieval: Scanning the product serial number instantly pulls up its complete build record, test history, and shipment details.
- Accurate Fault Diagnosis: Technicians can see which components were used, the solder profiles applied, and all test results, speeding up fault isolation.
- Warranty Validation: Quickly verify the manufacturing date and confirm if the product is within its warranty period.
- Trend Analysis: Aggregate RMA data with traceability records to identify recurring failures linked to specific component batches, processes, or design issues.
- Credible Customer Communication: Provide customers with data-backed explanations for failures, enhancing trust and transparency.
This capability turns a cost center (RMA handling) into a source of valuable quality intelligence.
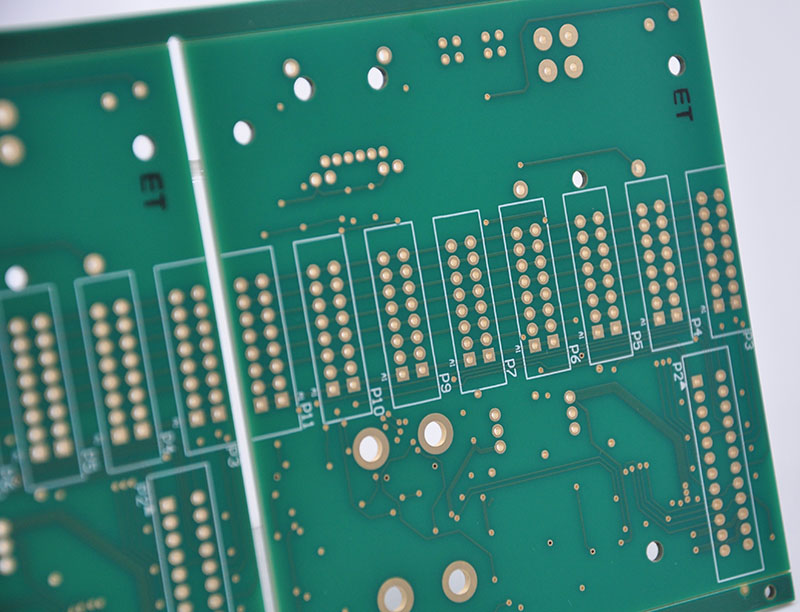
PCBA traceability is the indispensable framework for achieving reliable, high-quality, and compliant electronics manufacturing. This article has detailed its role in ensuring material integrity, process control, risk management, and post-market support.
At EBest Circuit (Best Technology), our commitment to deep, MES-driven PCBA traceability is what sets us apart. We empower our clients with full visibility in their supply chain, from component sourcing to final delivery. For further discussion, contact our team at sales@bestpcb.vn to discuss your project requirements.
FAQs
What Is A PCB Trace?
A PCB trace (or track) is the conductive copper pathway etched on a printed circuit board (PCB) that electrically connects components, forming the circuits. Understanding what is a pcb trace is fundamental to board design.
What Is The Difference Between PCB And PCBA?
A PCB (Printed Circuit Board) is the bare, unpopulated board. A PCBA (Printed Circuit Board Assembly) is the completed board after all electronic components have been soldered onto it. Traceability is critical at both stages.
What Are Common PCBA Defects?
Common defects include solder bridges (shorts), cold solder joints, tombstoning (component lifting), missing or misaligned components, and PCB trace damage like opens or cracks.
What Are The Main PCB Trace Types Used In Modern PCBs?
The primary PCB trace types are signal traces (for data/power), power planes (for stable voltage distribution), and ground planes (for return paths and shielding). Advanced designs use controlled impedance traces for high-speed signals.
How Do PCB Trace Tolerance Limits Impact Manufacturing Consistency?
PCB trace tolerance—the allowable deviation from the designed width or spacing—directly impacts electrical performance (e.g., impedance, current capacity). Tight, well-controlled tolerances, enabled by precise manufacturing and traceability, ensure consistent, reliable performance across all produced boards.
 language
language

