What is the Difference Between PCBA and PCB? PCB vs PCBA
Difference Between PCBA and The difference between PCBA and PCB comes down to function and manufacturing stage. A PCB (Printed Circuit Board) is the bare foundation of an electronic product. It consists of insulating material and patterned copper traces that define how signals flow, but it cannot operate on its own. PCBA is a PCB after electronic components are mounted and soldered. Once assembled, the board becomes electrically functional and ready for testing or integration into a product.

What is a PCB?
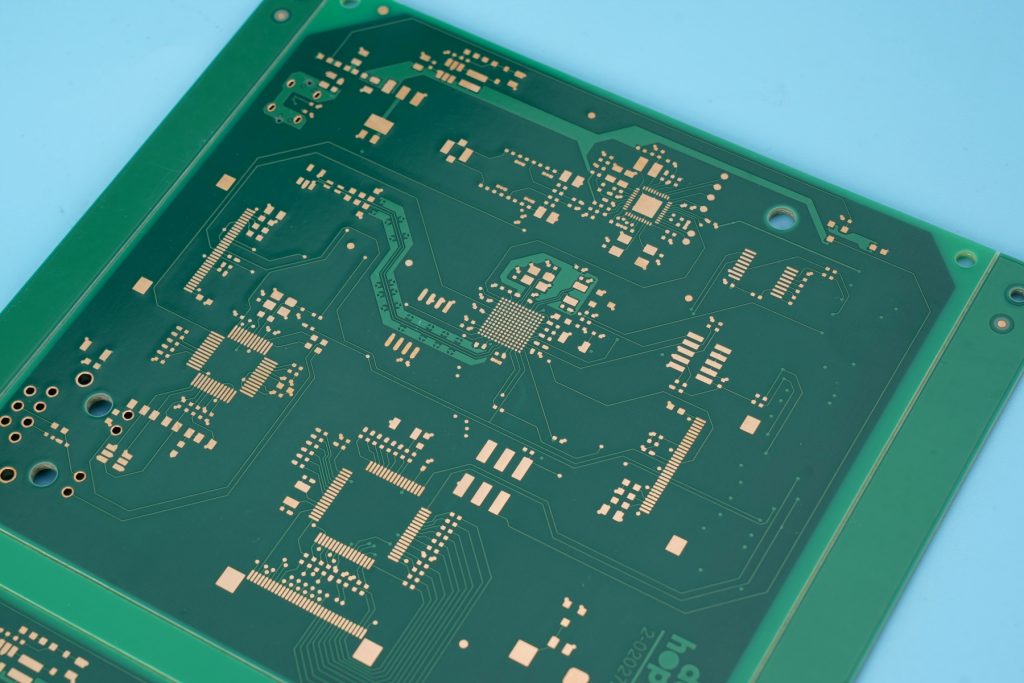
A PCB, short for Printed Circuit Board, is the physical foundation of nearly all electronic products. It is a flat board that supports and connects electronic components through copper pathways. On its own, a PCB does not perform any function. It only becomes functional after components are mounted and soldered.
A typical PCB consists of an insulating substrate, copper layers, surface finishes, and protective coatings. Designers use PCB layouts to define how electrical signals travel between components. These layouts directly affect signal integrity, heat dissipation, and product reliability.
In practical terms, a PCB is a bare board. It has no components installed. Manufacturers fabricate PCBs based on Gerber files, drill data, and stack-up requirements provided by the design team.
From a manufacturing view, PCB production focuses on accuracy, consistency, and material control. Trace width, spacing, hole size, and layer alignment all matter. Even small deviations can cause electrical failure later during assembly or testing.
What are the Different Types of PCBs?
PCBs come in many forms, each designed to meet specific electrical, mechanical, or thermal needs.
Common PCB types include:
- Single-layer PCB: One copper layer. Simple structure. Used in basic electronics and consumer devices.
- Double-layer PCB: Copper on both sides. More routing freedom. Widely used in industrial products.
- Multilayer PCB: Three or more copper layers. Supports dense circuits and high-speed signals.
- Rigid PCB: Solid and inflexible. Most common format in electronics.
- Flexible PCB: Made with flexible substrates. Ideal for tight spaces and moving parts.
- Rigid-flex PCB: Combines rigid and flexible sections. Reduces connectors and improves reliability.
- High-frequency PCB: Uses special materials for RF and microwave signals.
- Metal core PCB: Includes an aluminum or copper base for better heat transfer.
Each type impacts fabrication complexity, lead time, and cost. The PCB choice also affects how easy or difficult the later assembly stage will be.
What Does PCBA Mean?
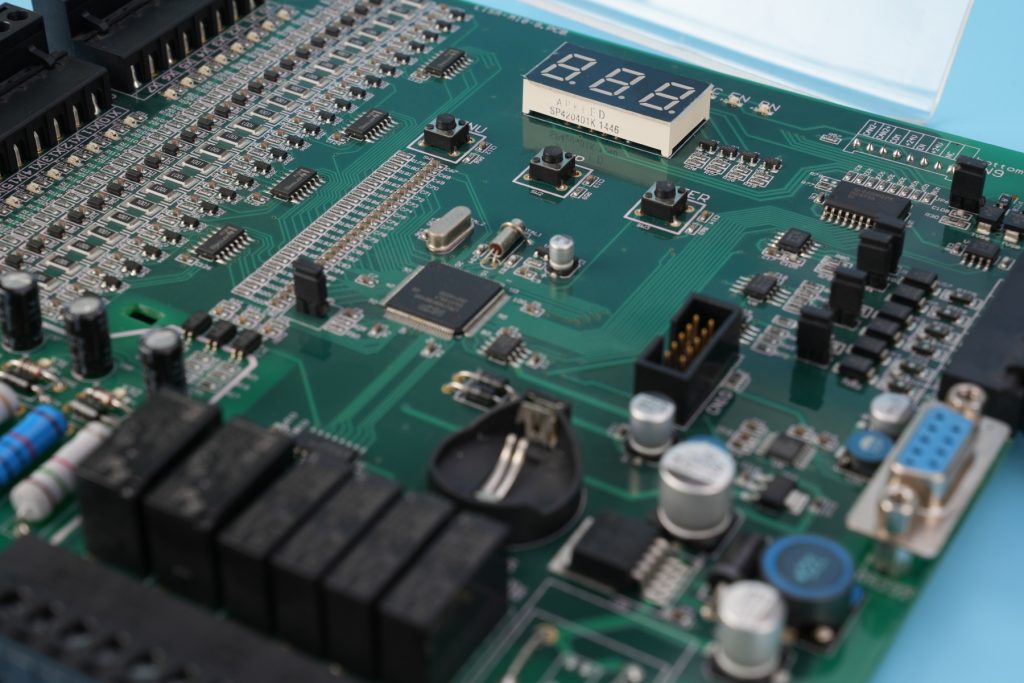
PCBA stands for Printed Circuit Board Assembly. It refers to a PCB after all electronic components have been mounted and soldered onto it. Once assembled, the board becomes a working electronic unit.
In simple terms, PCBA is the finished board, while PCB is only the base. PCBA includes components such as resistors, capacitors, ICs, connectors, and modules. It also includes solder joints, markings, and sometimes coatings.
The PCBA process transforms a static board into a functional product. This process requires not only machines, but also engineering control, quality systems, and testing methods.
What is the Difference Between a PCB and PCBA?
The difference between PCBA and PCB lies in function, value, and manufacturing scope. While they are related, they serve different roles in the product lifecycle.
A PCB is a passive structure. It has no electronic behavior. A PCBA is an active assembly that performs a specific task.
Key differences between PCB and PCBA include:
- Stage: PCB is an early manufacturing stage. PCBA is a later, more complete stage.
- Components: PCB has no components. PCBA includes all required electronic parts.
- Functionality: PCB cannot operate. PCBA can power on and perform functions.
- Manufacturing focus: PCB fabrication focuses on materials and precision. PCBA focuses on placement, soldering, and testing.
- Cost structure: PCB cost is mainly driven by material and layers. PCBA cost includes labor, components, and process control.
How Many Types of PCBA Are There?
PCBA types are usually defined by assembly technology and application needs. Each type has its own process flow and equipment requirements.
The most common PCBA types include:
- SMT PCBA: Uses surface mount components. High density. Automated process.
- THT PCBA: Uses through-hole components. Strong mechanical joints.
- Mixed-technology PCBA: Combines SMT and THT on the same board.
- Prototype PCBA: Low volume. Focus on speed and flexibility.
- Volume PCBA: Medium to high volume. Focus on efficiency and consistency.
- High-reliability PCBA: Built for medical, automotive, or aerospace use.
Each type requires different skills and controls. For example, SMT PCBA emphasizes placement accuracy and solder paste control, while THT PCBA often requires selective soldering or wave soldering.
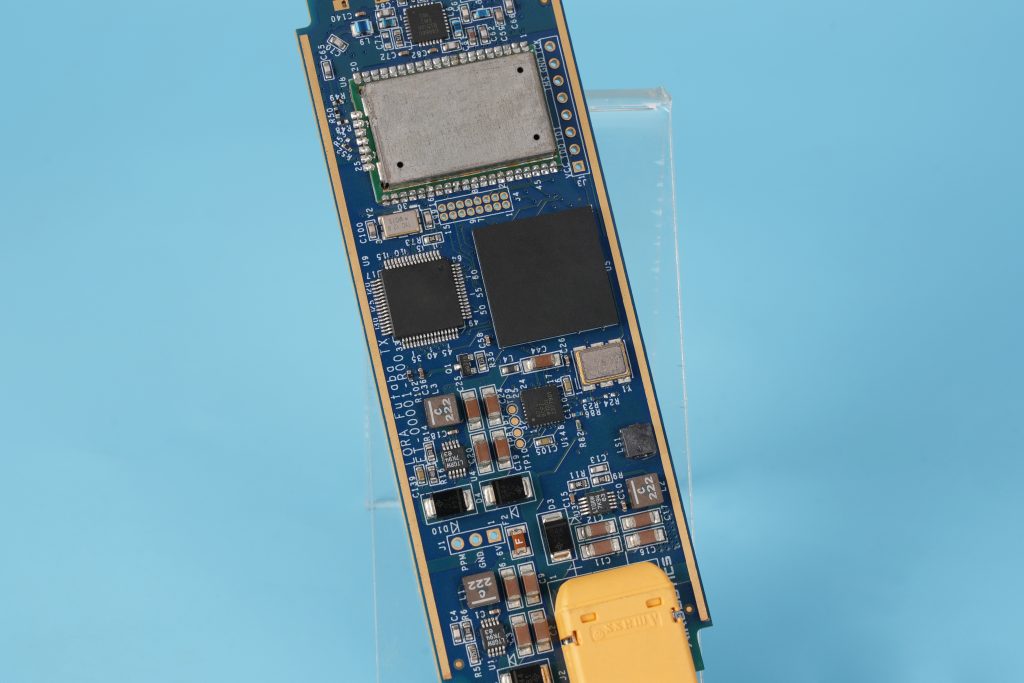
What is PCBA Made Of?
PCBA is made of a combination of materials, each serving a specific role. These materials must work together to ensure electrical performance and mechanical stability.
A complete PCBA includes:
- The PCB substrate, which supports everything
- Copper traces, which carry electrical signals
- Electronic components, which perform functions
- Solder, which creates electrical and mechanical connections
- Markings and labels, which aid identification
- Optional coatings, which protect against moisture and contamination
Material compatibility matters. Mismatch in thermal expansion or poor solder selection can reduce reliability. That is why experienced manufacturers pay close attention to material choices at both PCB and PCBA stages.
What Are the Key Components of a PCBA?
Components are the heart of any PCBA. They define what the board can do and how well it performs.
Typical PCBA components include:
- Resistors for current control
- Capacitors for energy storage and filtering
- Inductors for signal shaping
- Integrated circuits for logic and processing
- Connectors for external interfaces
- Sensors and modules for input and output
Each component must be correctly oriented, placed, and soldered. Even a small placement error can stop a board from working.
How Do You Test a PCBA?
Testing ensures that a PCBA works as intended and meets quality expectations. Good testing catches issues early, before boards reach final products or customers.
Common PCBA testing methods include:
- AOI (Automated Optical Inspection): Checks solder joints and placement accuracy.
- X-ray inspection: Inspects hidden solder joints, especially under BGAs.
- In-circuit testing (ICT): Verifies electrical connections and values.
- Functional testing: Confirms real-world operation.
- Burn-in testing: Detects early-life failures.
Not every project needs every test. The right mix depends on product complexity, industry standards, and risk tolerance. Testing adds value by improving yield and long-term reliability.
What Equipment Is Used in PCBA?
PCBA relies on a coordinated set of machines, each handling a specific step. Equipment quality directly affects assembly consistency.
Key PCBA equipment includes:
- Solder paste printers for accurate paste deposition
- Pick-and-place machines for component placement
- Reflow ovens for SMT soldering
- Wave or selective soldering machines for THT
- Inspection systems for quality control
- Testing fixtures and stations for verification
Behind the machines is process control. Parameters such as temperature profiles, placement speed, and inspection thresholds must be tuned and monitored.
Conclusion:
The difference between PCBA and PCB is simple but critical. A PCB is the bare board. A PCBA is the assembled, functional board. PCB focuses on structure. PCBA focuses on function.
For professional PCB and PCBA support, you can contact sales@bestpcb.vn
 language
language

