- +84-827-237566
- sales@bestpcb.vn
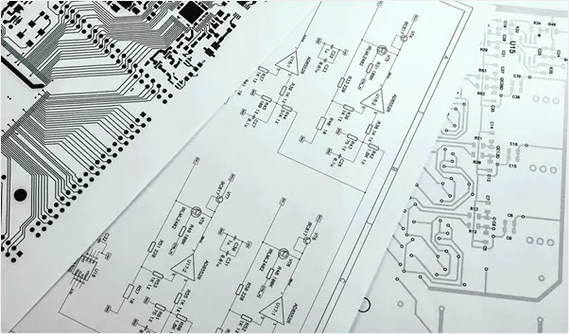
Printed circuit board (PCB) design is based on circuit schematics to realize the functions required by the circuit designer. This is a complex process that includes several steps, such as schematic drawing, layout design, DFM and testing.
A good PCB design can create functional, reliable, and cost-effective circuit boards that meet the electrical and physical requirements of the devices they will be used in. PCB design is critical to ensuring the proper operation of devices and minimizing the risks of electrical shorts, interference, and other problems that can arise from poor design. PCBs are widely used in various electronic devices, from small consumer products to large industrial machines.

Power Integrity (PI) Analysis focuses on managing the power distribution network to minimize noise, voltage drops, and other power-related issues. It involves evaluating the power distribution network within a PCB to ensure all components receive stable and adequate power.
Get instant quote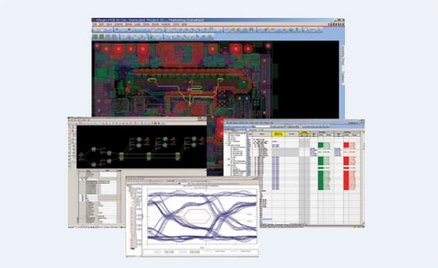
Signal Integrity (SI) Analysis can assess and optimize the quality of electrical signals as they travel through a PCB. It is mainly used to maintain the integrity of signals, especially in high-speed circuits, so that they can transmit without distortion or degradation. SI analysis solves issues such as signal reflection, crosstalk, and electromagnetic interference.
Get instant quote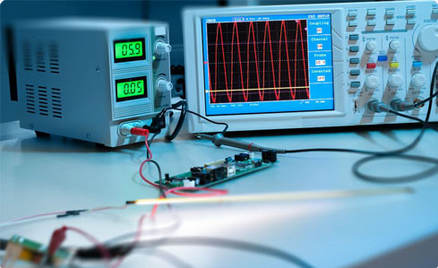
For every new PCB case, electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) is an important process in the development and certification of electronic devices. By evaluating a device's ability to function properly in its intended electromagnetic environment while limiting the unintentional generation, propagation, and reception of electromagnetic energy, we can make sure the device does not cause interference with other electronic equipment and can withstand external electromagnetic disturbances.
Get instant quote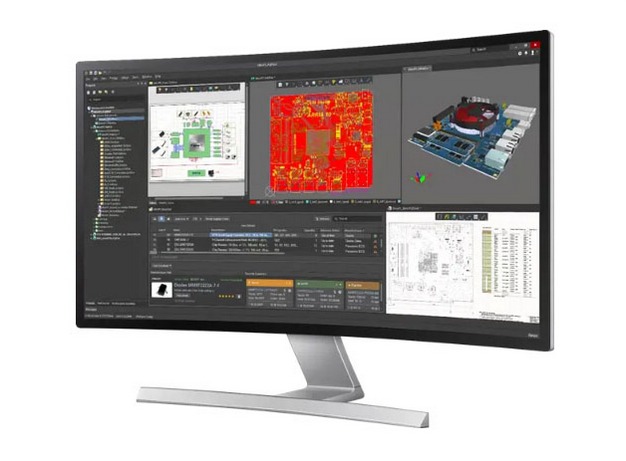
We uphold the following design principle: cost-effectiveness, security, compliance, performance, reliability and time to market.
Throughout the design process, we’ll collaborate with you on any required design changes and provide suggestions to improve your new product.
Full turnkey PCB design served for more than 1700 customers, include but are not limited to BYD, DIDI, HUAWEI.
Founded on June 28, 2006, Best Technology is committed to providing one-stop PCB solutions to drive technological advancement and innovation. With over 19 years of experience, we have become a trusted partner for clients worldwide, offering best solutions to meet the growing needs of the electronics industry.

Our products range from standard FR4 PCB, multi-layer PCBs, metal-based PCBs (MCPCBs), ceramic PCBs, flexible and rigid-flexible PCBs to high frequency PCBs. Currently our monthly capability is 260,000 square feet (28,900 square meter), more than 1,000 different boards will be completed. We also provide expedite service, so that urgent boards can be shipped out within 24 hours.
As a custom printed circuit board manufacturer, we believe that continuous growth is the key to success. So, we always invest heavily in research and development to stay ahead of industry trends. We focus on product quality and customer satisfaction, and we aim to build strong relationships and offer personalized support and solutions to our customers.

With 18 years of experience in PCB manufacturing and assembly, we offer competitive factory prices and short lead times to ensure your schedule runs smoothly.
We are committed to providing high-quality PCB solutions at competitive prices. By optimizing manufacturing processes and managing costs effectively, we ensure you receive the best value for your investment.
At Best Technology, quality is our top priority. We implement rigorous quality control processes throughout every stage of production, from raw material selection and prototyping to final product testing.
Our all-in-one approach simplifies the supply chain, shortens lead times, and improves communication efficiency. And we offer one-on-one sales assistant services to give you a superior experience working with us.
We understand the importance of meeting your project deadlines, and we provide online WIP updates to ensure you can track the progress of your PCB product.
Simply drop your email or phone number in the contact form, and we'll promptly provide you with a quotation.